Medical Instruments
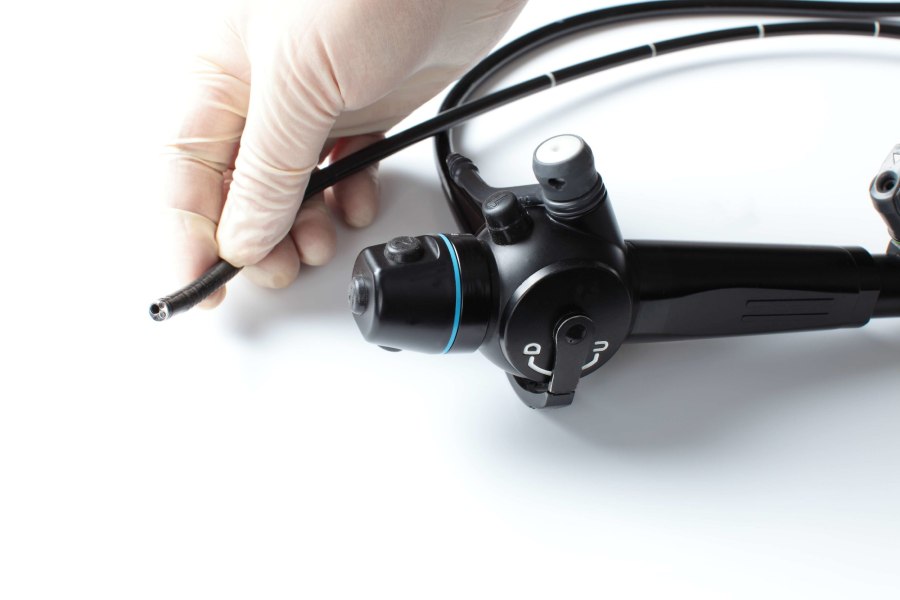
Fiber optics, commonly associated with internet and cable TV, have extensive applications in medicine. Their small size, resistance to electromagnetic interference, high durability, and non-toxic properties make them vital tools.
They are prominently utilized in minimally invasive surgery, endoscopes for internal imaging, and biomedical sensors for measurements like body temperature and heart rate.
Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT) employs fiber optics for 3-D imaging inside the body, aiding diagnoses like coronary artery disease. Notably, Harvard Medical School scientists are leveraging fiber optics to enhance tumor treatment and wound healing through photochemical tissue bonding.
These versatile fibers offer safer surgeries, quicker recoveries, and more comprehensive medical procedures.
 CUSTOM OPTICAL FILTERS
CUSTOM OPTICAL FILTERS
 OPTICAL WINDOWS
OPTICAL WINDOWS
 OPTICAL COATINGS
OPTICAL COATINGS
 UV OPTICS
UV OPTICS
 CYLINDRICAL OPTICS
CYLINDRICAL OPTICS
 CUSTOM TEMPERED OPTICS
CUSTOM TEMPERED OPTICS
 OPTICAL MIRRORS
OPTICAL MIRRORS
 NEUTRAL DENSITY
NEUTRAL DENSITY
 PRISMS & RETROREFLECTORS
PRISMS & RETROREFLECTORS
 ASSEMBLIES
ASSEMBLIES
 OPTICAL LENSES
OPTICAL LENSES
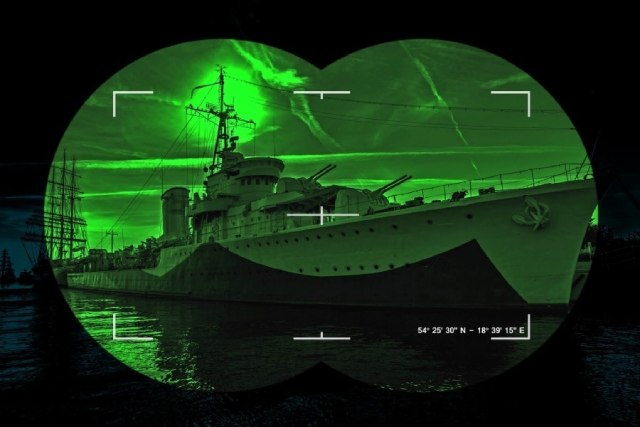 NIGHT VISION FILTERS
NIGHT VISION FILTERS
 ACHROMATIC LENSES
ACHROMATIC LENSES
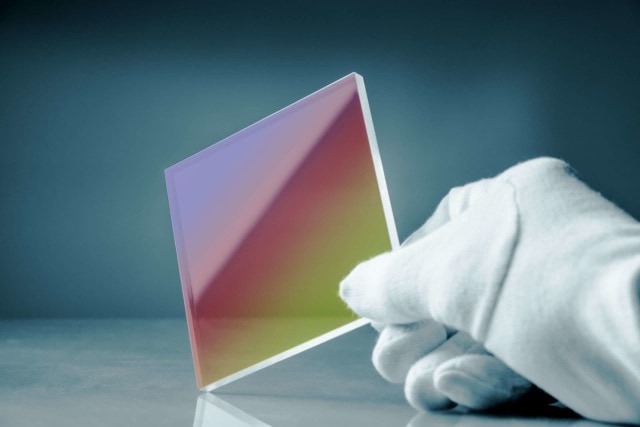 OPTICAL BEAM SPLITTERS
OPTICAL BEAM SPLITTERS